Autonomous vehicle sensors
The basic building blocks behind all autonomous and ADAS systems are sensors, which act as the vehicle’s “senses”. They enable the development of perception and provide information on the vehicle’s environment. Such sensors include radars, cameras, lidars, inertial sensors, and GNSS signal receivers. The properties of each sensor help understand and navigate the vehicle’s environment better. Read more…
Data fusion
Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to obtain a more stable, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any single source. Autonomous vehicles feature many independent sensors which can provide the same information directly or indirectly. Read more…
Localization
The vehicle’s localization algorithm is responsible for determining the positioning of the car relative to a selected reference system. Localization algorithms can be divided into 2 categories: relative and absolute reference system. Read more…
Mapping
In order to move through an unknown area, an autonomous vehicle needs a map, just like humans. Maps used for autonomy are more complex than those used by humans and are called HD (high definition) maps. Read more…
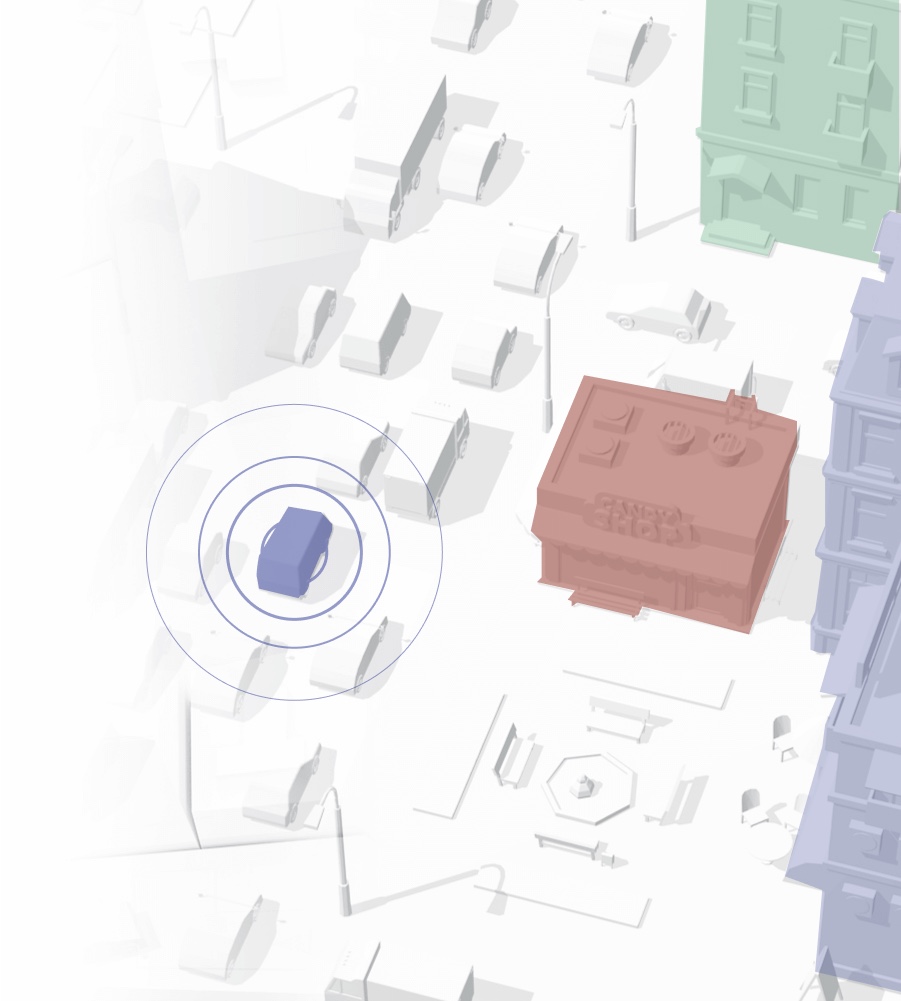
Object identification
While the vehicle is on the move, there are many other objects around it. These objects may or may not affect the vehicle’s route. Static objects can be localization waypoints or obstacles, while moving objects can result in a collision. In order to correctly determine the type of object in the vehicle’s environment, it must be properly identified. Read more…
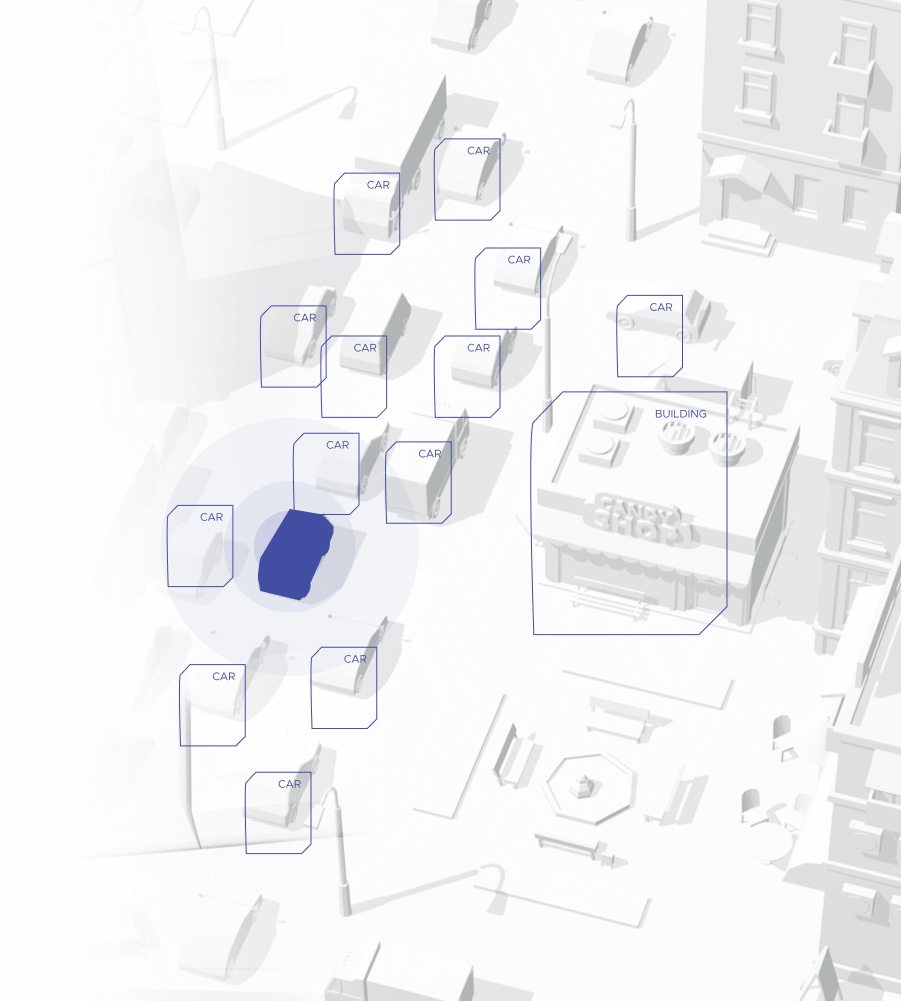
Object tracking
Object identification alone may not be enough to obtain a good autonomous system. Object detection involves the risk of false positive and false negative errors which can result in incorrect, or even dangerous, vehicle behavior. Usually, object identification also involves determining the confidence level (probability) of detecting a given object or assigning it to a given class of objects. Read more…
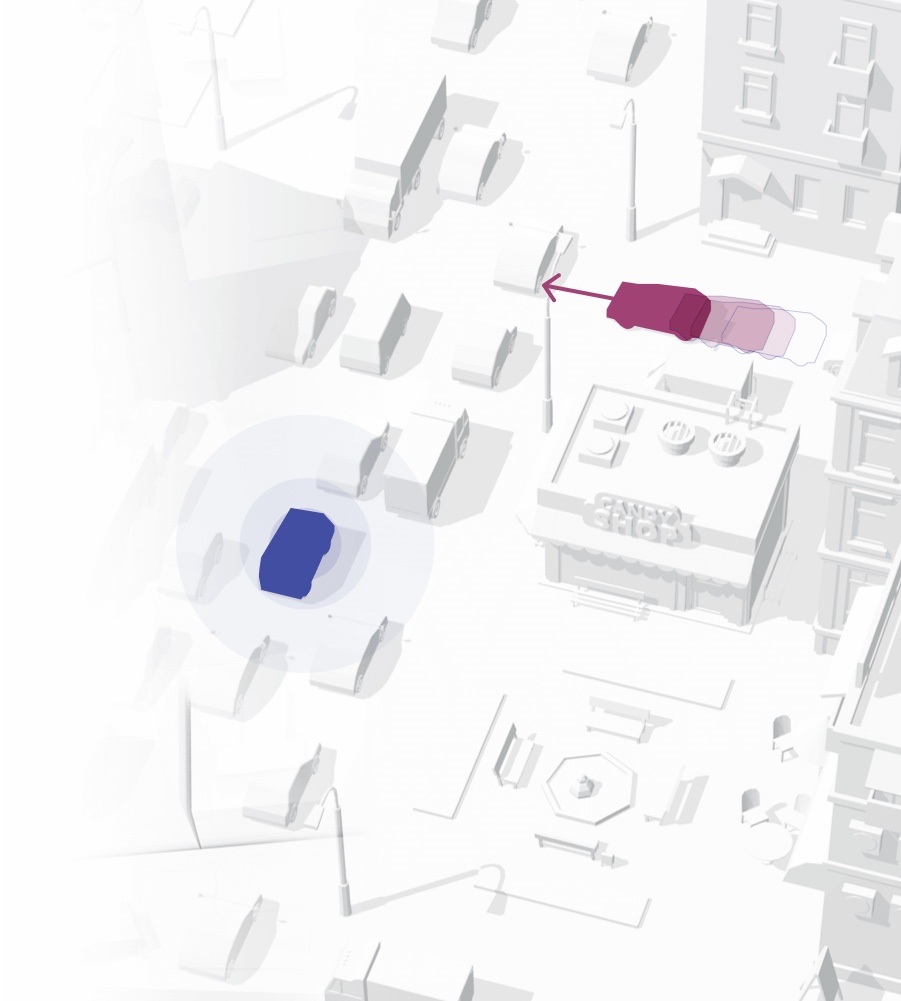
Trajectory planning
Successful control over an autonomous vehicle depends on multiple factors. One of them is the ability to determine a desired trajectory, i.e., path planning. The set trajectory is the currently desired path of movement over a short period of time. Its shape should be determined on an ongoing basis, adapting it to changing environmental conditions. Read more…